一、NioEventLoop与NioEventLoopGroup的关系

二、NioEventLoop
1. 设计原理
1. 负责IO读写
2. 执行task。通过调用NioEventLoop的execute(Runnable task)方法实现。我们知道,为了防止资源竞争和并发操作,我们经常会判断当前操作线程是否为EventLoop线程,如果不是,则将操作封装成task放进NioEventLoop的执行队列中,这样就实现了局部无锁化。
3. 定时任务。通过调用NioEventLoop的schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)方法实现。
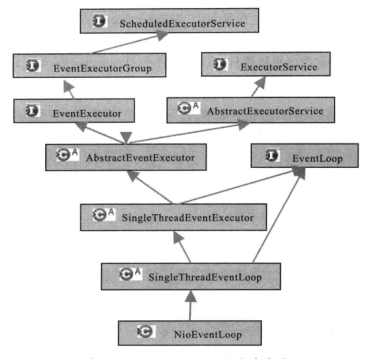
2. 继承关系类图
3. 成员变量及Selector初始化
这里可以看到,NioEventLoop持有一个Selector引用,负责去轮询准备就绪的Channel。
Selector selector;//多路复用器private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys;private final SelectorProvider provider;//selector生产者private Selector openSelector() { final Selector selector; try { // 1. 打开Selector selector = provider.openSelector(); } catch (IOException e) { throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e); } // 2. 是否打开SelectionKey优化,默认关闭,直接返回Selector if (DISABLE_KEYSET_OPTIMIZATION) { return selector; } // 3. 用自己的SelectedSelectionKeySet代替Java自带的selectedKeys try { SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet(); Class selectorImplClass = Class.forName("sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl", false, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()); // Ensure the current selector implementation is what we can instrument. if (!selectorImplClass.isAssignableFrom(selector.getClass())) { return selector; } Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys"); Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys"); selectedKeysField.setAccessible(true); publicSelectedKeysField.setAccessible(true); selectedKeysField.set(selector, selectedKeySet); publicSelectedKeysField.set(selector, selectedKeySet); selectedKeys = selectedKeySet; logger.trace("Instrumented an optimized java.util.Set into: {}", selector); } catch (Throwable t) { selectedKeys = null; logger.trace("Failed to instrument an optimized java.util.Set into: {}", selector, t); } return selector;} 4. run方法
NioEventLoop中最重要的方法,无限轮询准备好的Channel并处理。
首先将wakenUp还原为false,并保存之前的状态。通过hasTash()判断当前消息队列中是否有待处理消息,如果有则调用selectNow()方法立即进行一次select操作,看是否有准备就绪的Channel。
protected void run() { for (;;) { oldWakenUp = wakenUp.getAndSet(false); try { if (hasTasks()) { selectNow(); } else { select(); if (wakenUp.get()) { selector.wakeup(); } } ... selectorNow()方法会立即触发selector选择操作,如果由准备就绪的Channel,则返回就绪的Channel集合,否则返回0。操作完成之后,再次判断用户是否调用了Selector的wakenUp()方法,如果调用,则执行selector.wakenUp()操作。
void selectNow() throws IOException { try { selector.selectNow(); } finally { // restore wakup state if needed if (wakenUp.get()) { selector.wakeup(); } } } 如果消息队列中没有待处理消息,则执行select方法,由selector轮询,看是否由准备就绪的Channel。
private void select() throws IOException { Selector selector = this.selector; try { int selectCnt = 0; long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime(); // 当前时间 + 定时任务延时时间 = 定时任务触发事件 long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos); for (;;) { // 超时时间 = 定时任务触发时间 - 当前时间 + 0.5毫秒调整值 --> 转化为毫秒 long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L; // 如果需要立即执行(已超时),则轮询 if (timeoutMillis <= 0) { if (selectCnt == 0) { selector.selectNow(); selectCnt = 1; } break; } // 阻塞timeout时间,等待定时任务,执行select int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis); selectCnt ++; if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks()) { // 有新事件待处理 || 用户调用了wakenUp()唤醒多路复用器 || 消息队列中有新任务 break; } // 如果本次是空轮询,有可能出发了JDK的epoll bug,它会导致selector空轮询,使IO线程一直处于100%状态 // 对空轮询进行判断,如果在一定周期内连续发生了N次空轮询,说明触发了bug // 需要重建selector,将原selector上的Channel注册到新的selector上,并将老selector关闭 if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 && selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) { // The selector returned prematurely many times in a row. // Rebuild the selector to work around the problem. logger.warn( "Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding selector.", selectCnt); rebuildSelector(); selector = this.selector; // Select again to populate selectedKeys. selector.selectNow(); selectCnt = 1; break; } currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime(); } if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row.", selectCnt - 1); } } } catch (CancelledKeyException e) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector - JDK bug?", e); } // Harmless exception - log anyway }} 如果轮询到了处于就绪状态的SocketChannel,则需要处理IO事件。
处理完IO事件后,NioEventLoop还需要处理非IO的task和定时任务。为了保证IO事件和task都有足够的CPU事件执行,这里用IO事件占比计算非IO事件的执行事件(默认50%),在执行task时,如果超过这个时间,则直接返回,队列中的任务留到以后执行(这里Netty为了提升性能,每执行60次判断一次超时时间)。
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();needsToSelectAgain = false;// 根据是否优化selectionKey执行不同的处理方法(都是处理IO事件)if (selectedKeys != null) { processSelectedKeysOptimized(selectedKeys.flip());} else { processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());}final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;// 根据IO执行时间得到非IO执行时间,然后取执行taskrunAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) { // 从定时任务队列中将task放到tskQueue中(这里拿的是正在过期的任务) fetchFromDelayedQueue(); // 从taskQueue中拿task Runnable task = pollTask(); if (task == null) { return false; } final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos; long runTasks = 0; long lastExecutionTime; for (;;) { try { task.run(); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("A task raised an exception.", t); } runTasks ++; // 为了提升性能,每执行60次,判断一次超时时间,如果执行时间已超出系统给定时间,则退出 if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) { lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime(); if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) { break; } } // 循环处理task,如果没task了则退出 task = pollTask(); if (task == null) { lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime(); break; } } this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime; return true;} 最后,判断系统是否处于停机状态,如果是,则调用closeAll方法释放资源,令NioEventLoop退出循环,关闭线程。
if (isShuttingDown()) { closeAll(); if (confirmShutdown()) { break; } } closeAll()方法遍历获取所有Channel,调用它的Unsafe.close()方法关闭所有链路,释放资源(具体close()方法可以看前面的Unsafe源码分析,close()方法最终调用的还是javaChannel的close()方法)。
private void closeAll() { selectAgain(); Set keys = selector.keys(); Collection channels = new ArrayList (keys.size()); for (SelectionKey k: keys) { Object a = k.attachment(); if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { channels.add((AbstractNioChannel) a); } else { k.cancel(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") NioTask task = (NioTask ) a; invokeChannelUnregistered(task, k, null); } } for (AbstractNioChannel ch: channels) { ch.unsafe().close(ch.unsafe().voidPromise()); }} 三、NioEventLoopGroup
1. 构造方法(NioEventLoop创建)
我们先来看EventLoopGroup的构造方法,这里通过构造方法,创建了指定线程数的NioEventLoop。
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) { this(nThreads, (Executor) null); } public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) { this(nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider()); } public NioEventLoopGroup( int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) { super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider); } // DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = CPU个数*2 protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) { super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args); } protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) { if (nThreads <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads)); } if (executor == null) { executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory()); } // EventLoop数组 children = new EventExecutor[nThreads]; for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) { boolean success = false; try { children[i] = newChild(executor, args); success = true; } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e); } finally { if (!success) { for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) { children[j].shutdownGracefully(); } for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) { EventExecutor e = children[j]; try { while (!e.isTerminated()) { e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } catch (InterruptedException interrupted) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); break; } } } } } protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception { return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0]); } 2. NioEventLoop的分配
当一个新的Channel连接时,NioEventLoopGroup需要拿出一个NioEventLoop让Channel绑定,这个Channel之后的IO操作都在这个NioEventLoop上操作。
public EventExecutor next() { return children[Math.abs(childIndex.getAndIncrement() % children.length)]; }